---
title: 'Get started with Cursor and Neon Postgres MCP Server'
subtitle: 'Make schema changes with natural language using Cursor and Neon MCP Server'
author: dhanush-reddy
enableTableOfContents: true
createdAt: '2025-02-20T00:00:00.000Z'
updatedOn: '2025-02-20T00:00:00.000Z'
---
Imagine adjusting your database schema simply by describing the change in plain English. This is possible by combining [Cursor](https://cursor.com) with the [Neon MCP Server](https://github.com/neondatabase/mcp-server-neon).
This guide demonstrates how to use [Cursor's Composer](https://docs.cursor.com/composer) and Neon's MCP server to perform database migrations in your Neon project.
The Neon MCP Server grants powerful database management capabilities through natural language requests. **Always review and authorize actions requested by the LLM before execution.** Ensure that only authorized users and applications have access to the Neon MCP Server.
The Neon MCP Server is intended for local development and IDE integrations only. **We do not recommend using the Neon MCP Server in production environments.** It can execute powerful operations that may lead to accidental or unauthorized changes.
For more information, see [MCP security guidance →](/docs/ai/neon-mcp-server#mcp-security-guidance).
## Key components
Let's break down the key components in this setup:
- **Cursor**: Cursor is an AI-first code editor that supports Model Context Protocol (MCP) for interfacing with external tools (APIs, databases, etc.)
- **Neon MCP Server**: Neon's MCP server acts as a bridge between MCP clients like Cursor and [Neon's API](https://api-docs.neon.tech/reference/getting-started-with-neon-api), letting you work with Neon databases using natural language commands.
- **Model Context Protocol (MCP)**: MCP is a lightweight communication standard that allows Cursor and Neon MCP Server to work together.
## Setting up Neon MCP Server in Cursor
You have two options for connecting Cursor to the Neon MCP Server:
1. **Remote MCP Server:** Connect to Neon's managed MCP server using OAuth for authentication. This method is more convenient as it eliminates the need to manage API keys in Cursor. Additionally, you will automatically receive the latest features and improvements as soon as they are released.
2. **Local MCP Server:** Run the Neon MCP server locally on your machine, authenticating with a Neon API key.
### Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
1. **Cursor Editor:** Download and install Cursor from [cursor.com](https://cursor.com).
2. **A Neon Account and Project:** You'll need a Neon account and a project. You can quickly create a new Neon project here [pg.new](https://pg.new)
3. **Neon API Key (for Local MCP server):** After signing up, get your Neon API Key from the [Neon console](https://console.neon.tech/app/settings/api-keys). This API key is needed to authenticate your application with Neon. For instructions, see [Manage API keys](/docs/manage/api-keys).
Keep your Neon API key secure, and never share it publicly. It provides access to your Neon projects.
4. **Node.js (>= v18) and npm:** Ensure Node.js (version 18 or later) and npm are installed. Download them from [nodejs.org](https://nodejs.org).
### Quick Setup (Recommended)
The fastest way to get started is with the [`neonctl init`](/docs/reference/cli-init) command, which automates OAuth authentication, API key creation, and Cursor configuration:
```bash
npx neonctl@latest init
```
This command authenticates via OAuth, creates an API key, and configures Cursor to connect to Neon's remote MCP server. API key authentication means **fewer approval prompts** when using MCP tools. Once complete, ask your AI assistant **"Get started with Neon"**.
Cursor offers a deep link for quick OAuth setup:
 Note: This uses OAuth (not API key), so you'll need to approve each MCP action. For fewer prompts, use Quick Setup above.
### Option 1: Setting up the Remote Hosted Neon MCP Server (OAuth)
By default, the Remote MCP Server connects to your personal Neon account. To connect to an organization's account, you must authenticate with an API key. For more information, see [API key-based authentication](/docs/ai/neon-mcp-server#api-key-based-authentication).
This method uses Neon's managed server and OAuth authentication.
1. Open Cursor.
2. Create a `.cursor` directory in your project's root directory. This is where Cursor will look for the MCP server configuration.
3. Paste the following JSON configuration into a file named `mcp.json` in the
`.cursor` directory:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"url": "https://mcp.neon.tech/mcp",
"headers": {}
}
}
}
```
If you have other MCP servers configured, you can copy just the `Neon` part.
Save the `mcp.json` file after pasting the configuration.
4. **Restart Cursor** or reload the window (`Developer: Reload Window` from the Command Palette). If Cursor prompts you to Enable the MCP server, click **Enable**.
5. An OAuth window will open in your browser. Follow the prompts to authorize Cursor to access your Neon account.
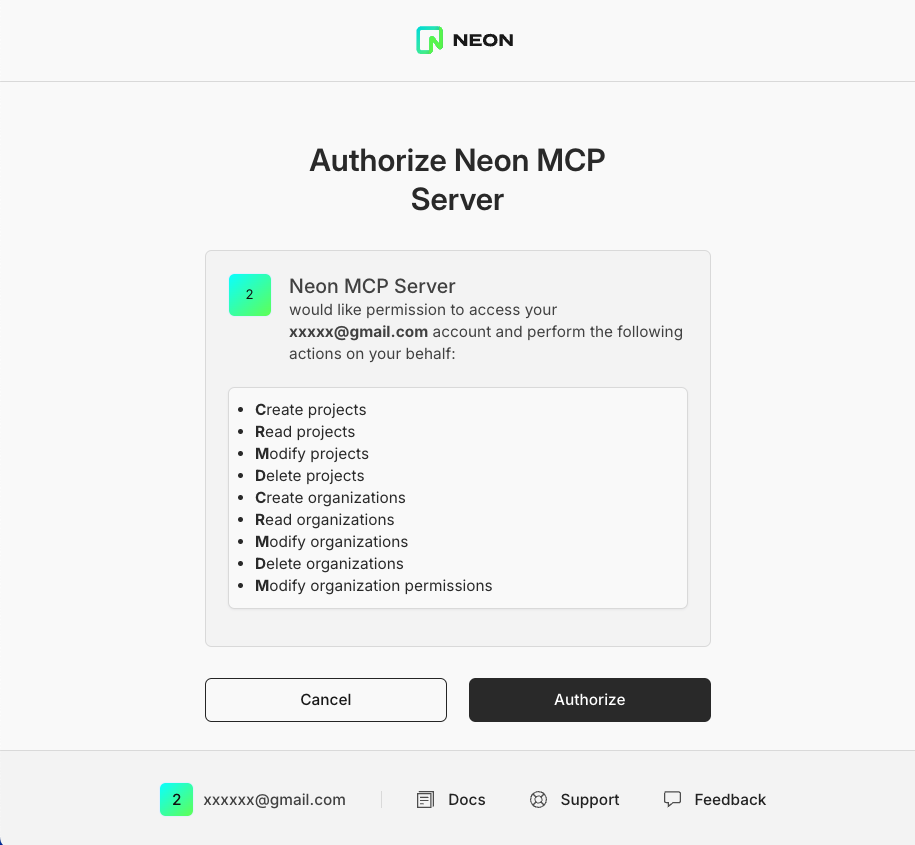
6. You can verify that the connection is successful by checking the **Tools & MCP** section in Cursor settings.
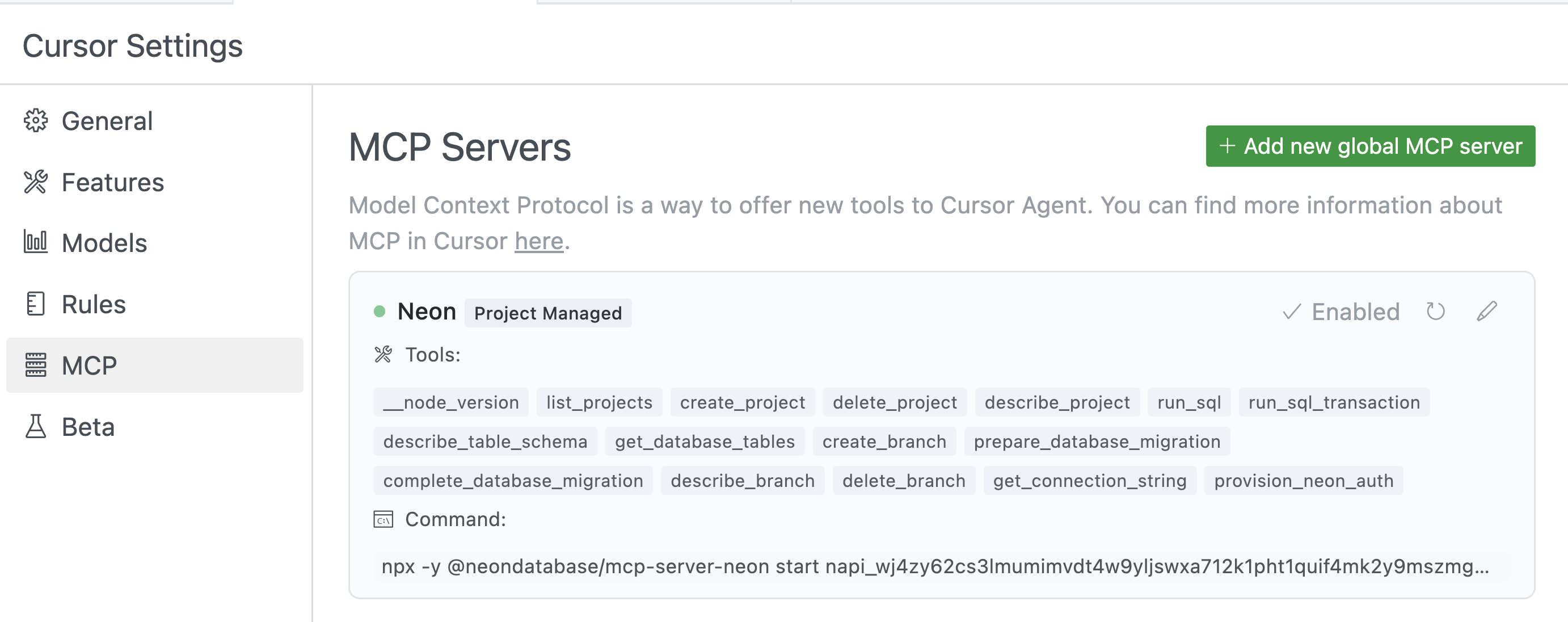
7. Cursor is now connected to Neon's remote MCP server.
### Option 2: Setting up the Local Neon MCP Server
This method runs the Neon MCP server locally on your machine, using a Neon API key for authentication.
1. Open Cursor.
2. Create a `.cursor` directory in your project's root directory. This is where Cursor will look for the MCP server configuration.
3. Paste the following JSON configuration into a file named `mcp.json` in the `.cursor` directory. Replace `` with your actual Neon API key which you obtained from the [prerequisites](#prerequisites) section:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@neondatabase/mcp-server-neon", "start", ""]
}
}
}
```
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": [
"/c",
"npx",
"-y",
"@neondatabase/mcp-server-neon",
"start",
""
]
}
}
}
```
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"command": "wsl",
"args": ["npx", "-y", "@neondatabase/mcp-server-neon", "start", ""]
}
}
}
```
If you have other MCP servers configured, you can copy just the `Neon` part.
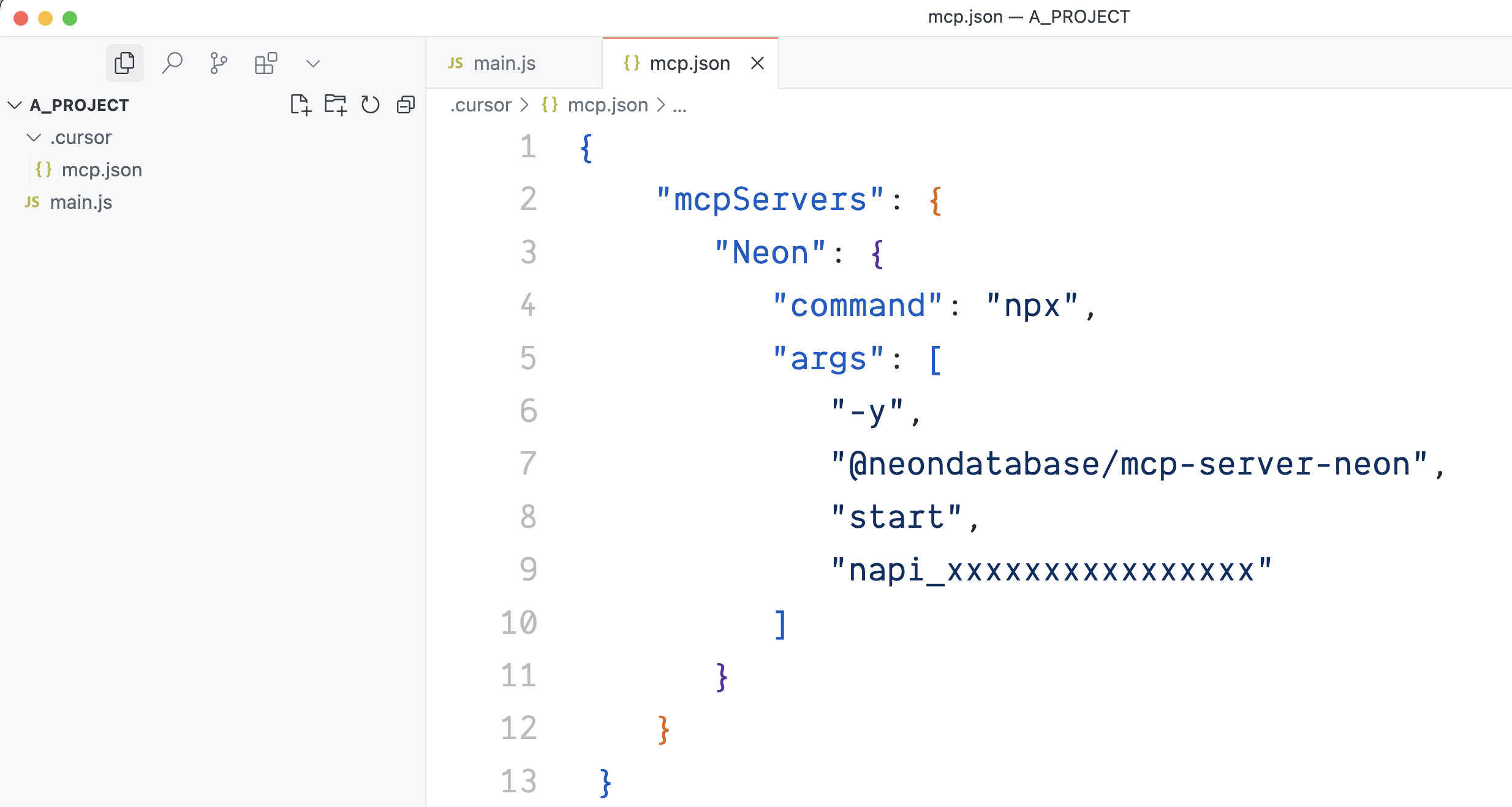
4. Save the `mcp.json` file after pasting the configuration.
5. **Restart Cursor** or reload the window (`Developer: Reload Window` from the Command Palette).
6. Cursor is now connected to Neon's MCP server. You can verify that the connection is successful by checking the **MCP Servers** section in Cursor settings.

You've now configured Neon MCP Server in Cursor and can manage your Neon Postgres databases using AI.
### Verification
Now that you have the Neon MCP server set up either remotely or locally, you can verify the connection and test the available tools.
1. Open a Cursor **Chat** using the keyboard shortcut **Command + I** (on Mac) or **Control + I** (on Windows) and select the **Agent** option from the drop-down menu.
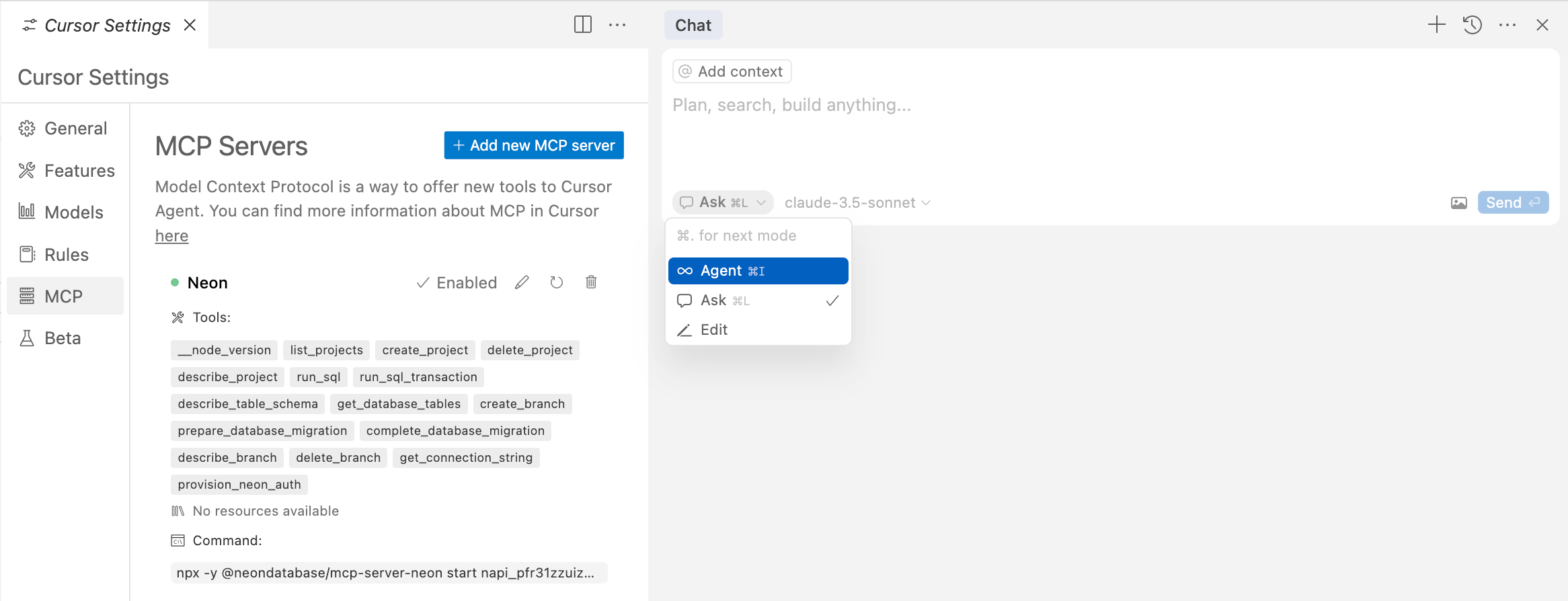
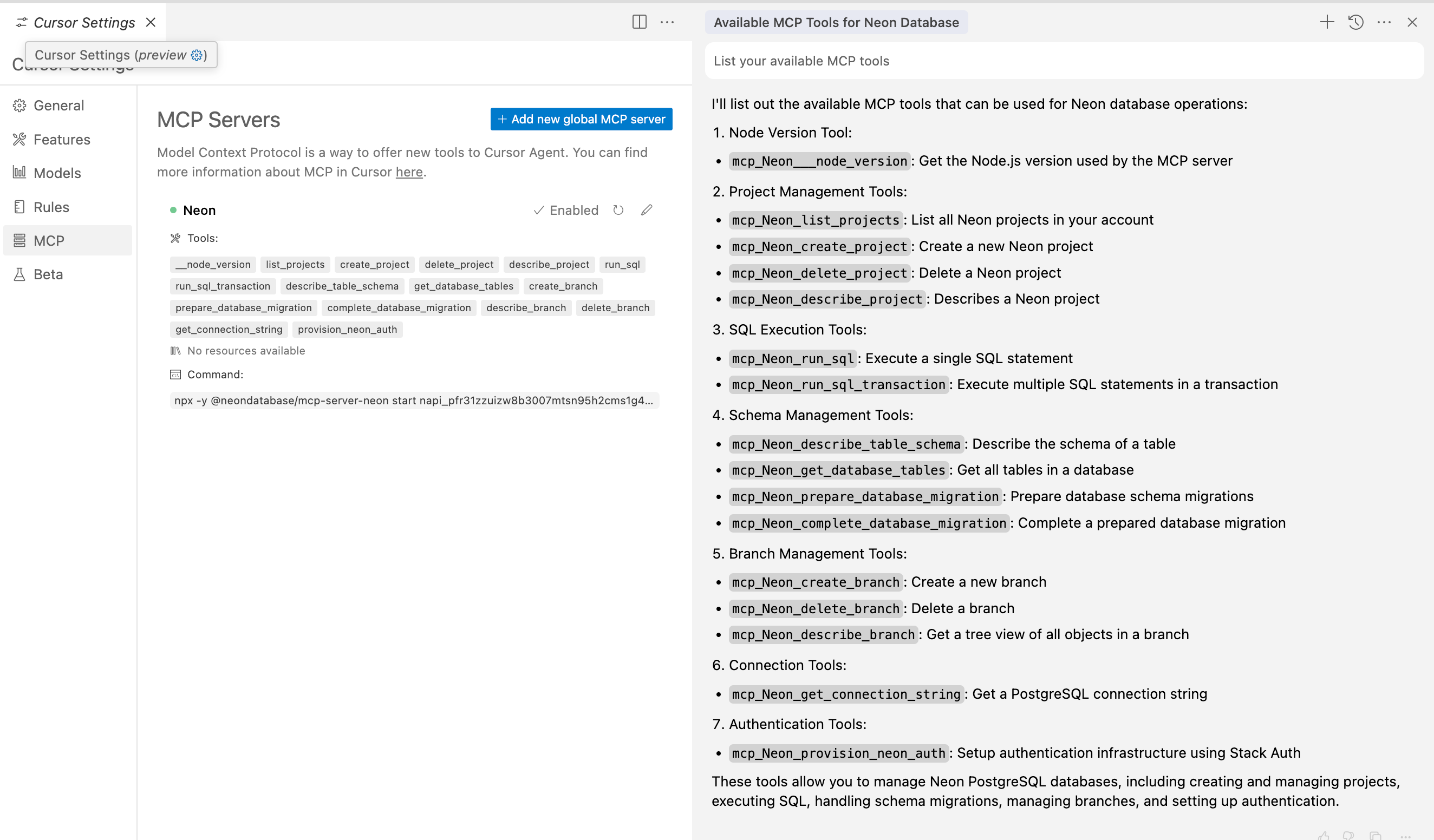
2. Type `List your available MCP tools` in the Composer text field, select the **agent** option in the corner of the field, and click **Submit**.
**_Note: The agent option here is tiny and easy to miss!_**
3. Try out an Neon MCP Server tool by typing `Tell me about my Neon project `. **You'll need to provide your Neon project ID.**
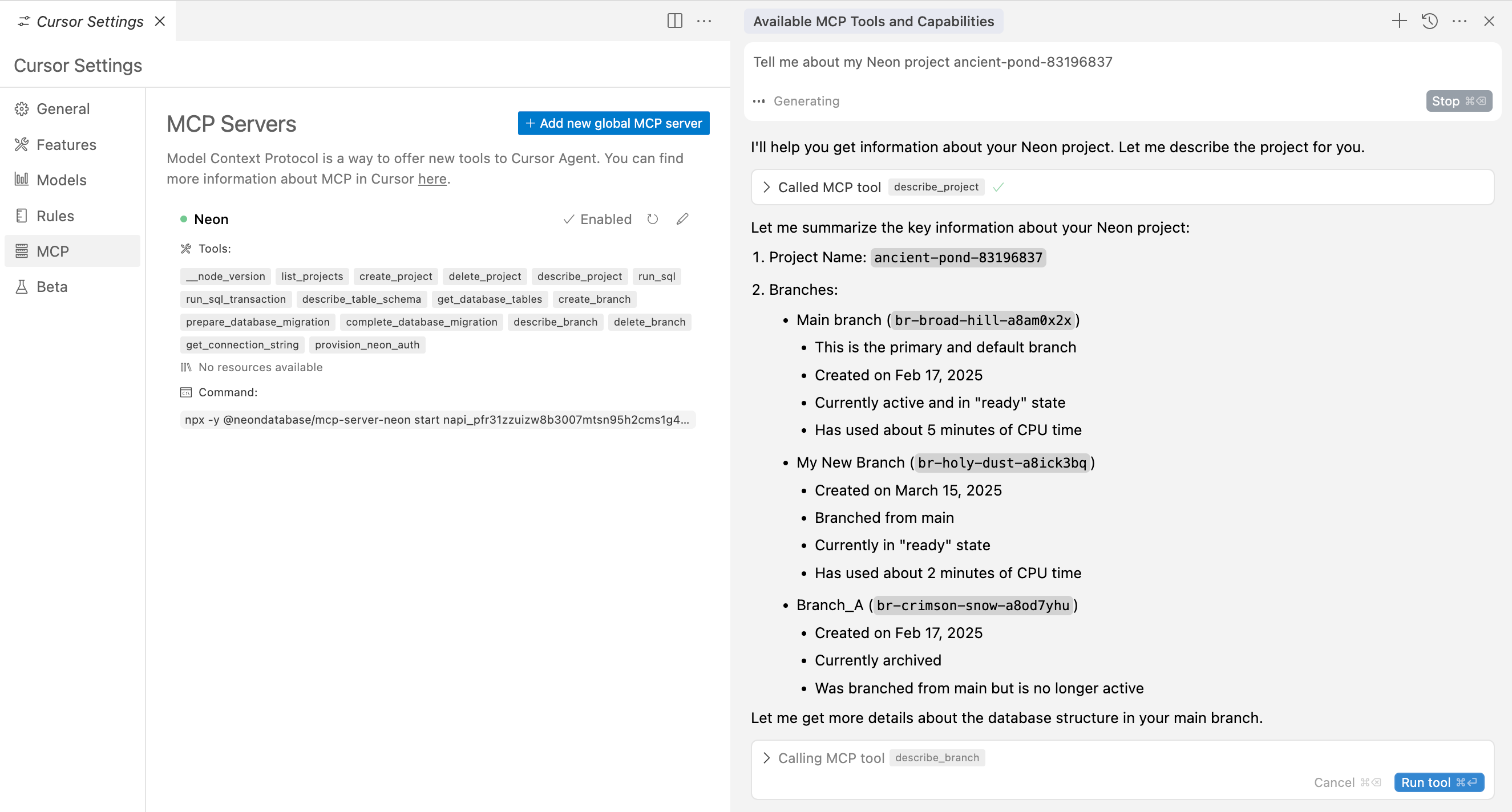
Cursor uses the Neon MCP Server `describe_project` tool to retrieve your project's details.
### Global MCP Server in Cursor
You can also set up a global MCP server in Cursor. This allows you to use the same MCP server configuration across all your projects. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Open Cursor.
2. Go to the **Settings**.
3. In the **Tools & MCP** section, click on **+ Add Custom MCP**.
4. Paste the same JSON configuration either for the **Remote Hosted** or **Local MCP Server** (as shown in the previous sections) into the configuration field.
5. Save the configuration.
6. Restart Cursor or reload the window (`Developer: Reload Window` from the Command Palette).
7. You now have Neon MCP Server set up globally in Cursor. You can use it in any project without needing to configure it again for each project.
### Troubleshooting
If you are on a version of Cursor that does not support JSON configuration for MCP servers, you can use the following command when prompted:
```bash
npx -y @neondatabase/mcp-server-neon start
```
These actions enable any MCP client like Cursor to interact with various functionalities of the **Neon platform via the Neon API.** Certain tools, especially database migration ones, are tailored for AI agent and LLM usage, leveraging Neon’s branching for safe preview and commit.
## Development Workflow: Adding a Column with Cursor and Neon MCP
Let's walk through a typical development scenario: Quickly adding a column for prototyping using natural language within Cursor. The following chat log demonstrates a real interaction with Cursor and the Neon MCP server.
**Scenario:** During development, you decide to track timestamps for entries in your `playing_with_neon` table. You want to quickly add a `created_at` column.
Use `⌘I` to open Cursor's Composer and `⌘N` to create a new Composer.
For your security, review the tool's purpose before permitting the operation to proceed. Remember that LLMs can sometimes produce unexpected results, so careful monitoring is always recommended.
Here's the conversation log between the user and Cursor:
```text shouldWrap
User: In my neon project id: round-salad-44063611 list all the tables
Cursor: I'll help you list all the tables in your Neon project. I'll use the default database name 'neondb' since none was specified.
> Called MCP Tool (get_database_tables)
> I found one table in your database:
> playing_with_neon (in the public schema)
> Would you like to see more details about this table's structure or perform any other operations with it?
User: Can you show me first 5 rows?
Cursor: I'll query the first 5 rows from the playing_with_neon table.
> Called MCP Tool (run_sql)
> Here are the first 5 rows from the table. The table has three columns:
> id (sequential numbers)
> name (string values)
> value (decimal numbers)
> Would you like to perform any other operations with this data?
User: can you add a created_at column?
Cursor: I'll help you add a created_at column to the playing_with_neon table. I'll set it up with a timestamp data type and set it to automatically record the creation time of new rows.
> Called MCP Tool (prepare_database_migration)
> Let me verify the change in the temporary branch to make sure it was applied correctly.
> Called MCP Tool (run_sql)
> I've added the created_at column to the playing_with_neon table in a temporary branch. Would you like to commit this migration to the production branch?
> Migration Details:
> Migration ID: a65babcd-d1cc-401f-89b5-762570570102
> Temporary Branch Name: br-silent-cherry-a1eqrl6i
> Temporary Branch ID: br-silent-cherry-a1eqrl6i
> Migration Result: Success
> Please let me know if you'd like to proceed with applying this change to the production branch.
User: yeah do it
Cursor: I'll complete the migration and apply the changes to the production branch.
> Called MCP Tool (complete_database_migration)
> The migration has been successfully completed! The created_at column has been added to your table in the production branch, and the temporary branch has been cleaned up.
```
**Key takeaways:**
- **Natural language interaction:** You can use simple, conversational English to interact with your database.
- **Step-by-step guidance:** Cursor (Claude) confirms each step and provides details like branch names and migration IDs.
- **MCP Tools in Action:** The underlying MCP tools (`get_database_tables`, `run_sql`, `prepare_database_migration`, `complete_database_migration`) illustrate the automated process.
- **Branching for safety:** The agent automatically creates a temporary branch for schema changes. The user will be prompted to confirm the migration before applying it to the production branch.
You can verify the changes in your Neon Console or by querying the database directly.
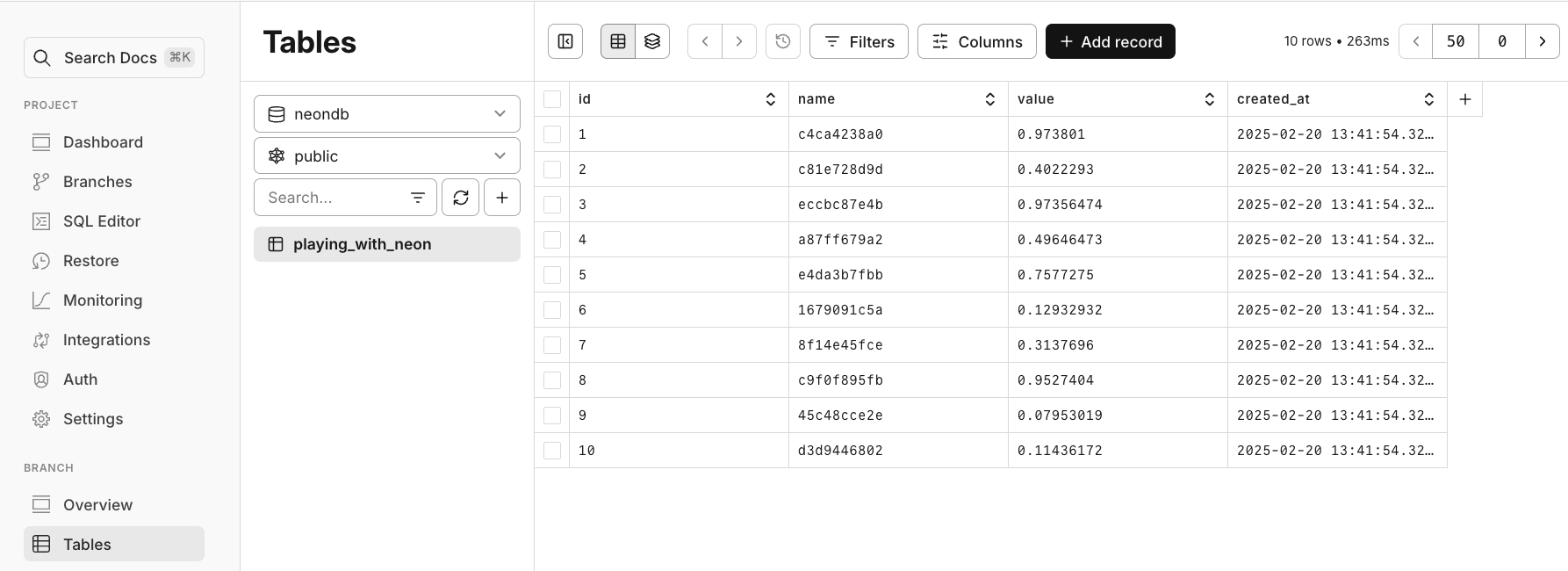
While the Neon MCP server allows you to utilize all of Neon's functionalities, you can also use a [generic Postgres MCP server](https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/servers/tree/main/src/postgres) to connect to Neon.
## Bonus: Creating a project and branch
Beyond schema changes, you can also manage your Neon projects and branches directly within Cursor using natural language commands. This can be useful for quickly setting up a new development or test environment.
### Creating a new project
Let's say you want to create a new Neon project named "my-new-project". You can simply tell Cursor:
```text shouldWrap
User: Create a Neon project named "my-new-project"
Cursor: I'll help you create a new Neon project with the specified name.
> Called MCP Tool (create_project)
> Great! I've created a new Neon project for you with the name "my-new-project". Here are the important details:
> Project ID: orange-dawn-33739962
> Default branch: main
> Default database: neondb
> The project is ready to use. You can start creating tables and working with your database right away.
```
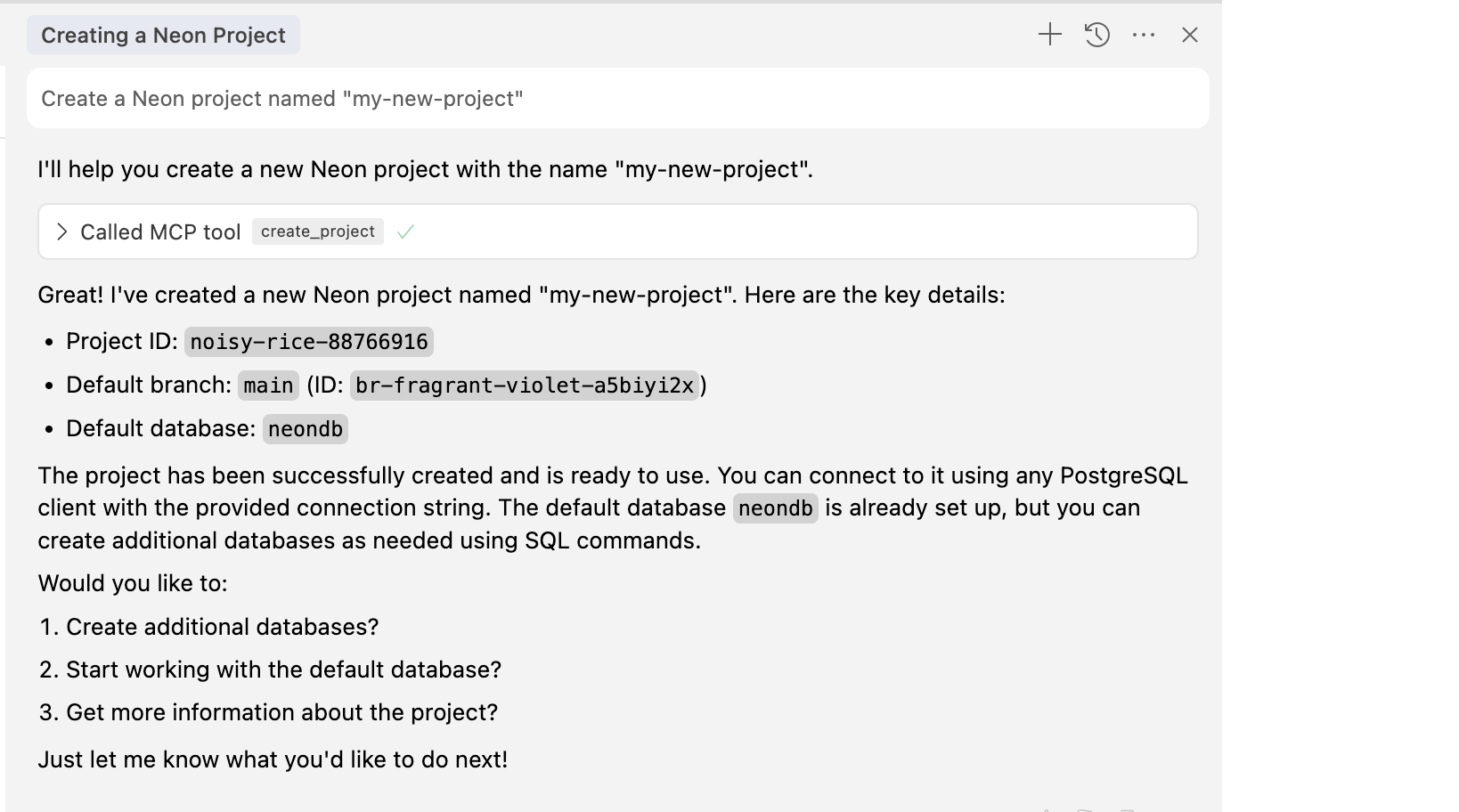
Cursor will then use the `create_project` MCP tool to initiate the project creation. It will provide you with a project ID and name.
### Creating a New Branch
Once you have a project, you can easily create new branches for development or experimentation. For example, to create a branch named "feature-x" in your "my-new-project" project:
```text shouldWrap
User: Create a branch named "feature-x"
Cursor: Perfect! I've created a new branch named "feature-x". Here are the details:
> Branch ID: br-cold-mountain-a523ka2w
> Branch name: feature-x
> Parent branch ID: br-odd-pine-a5y53krm
> The branch has been created successfully and is ready for use.
```
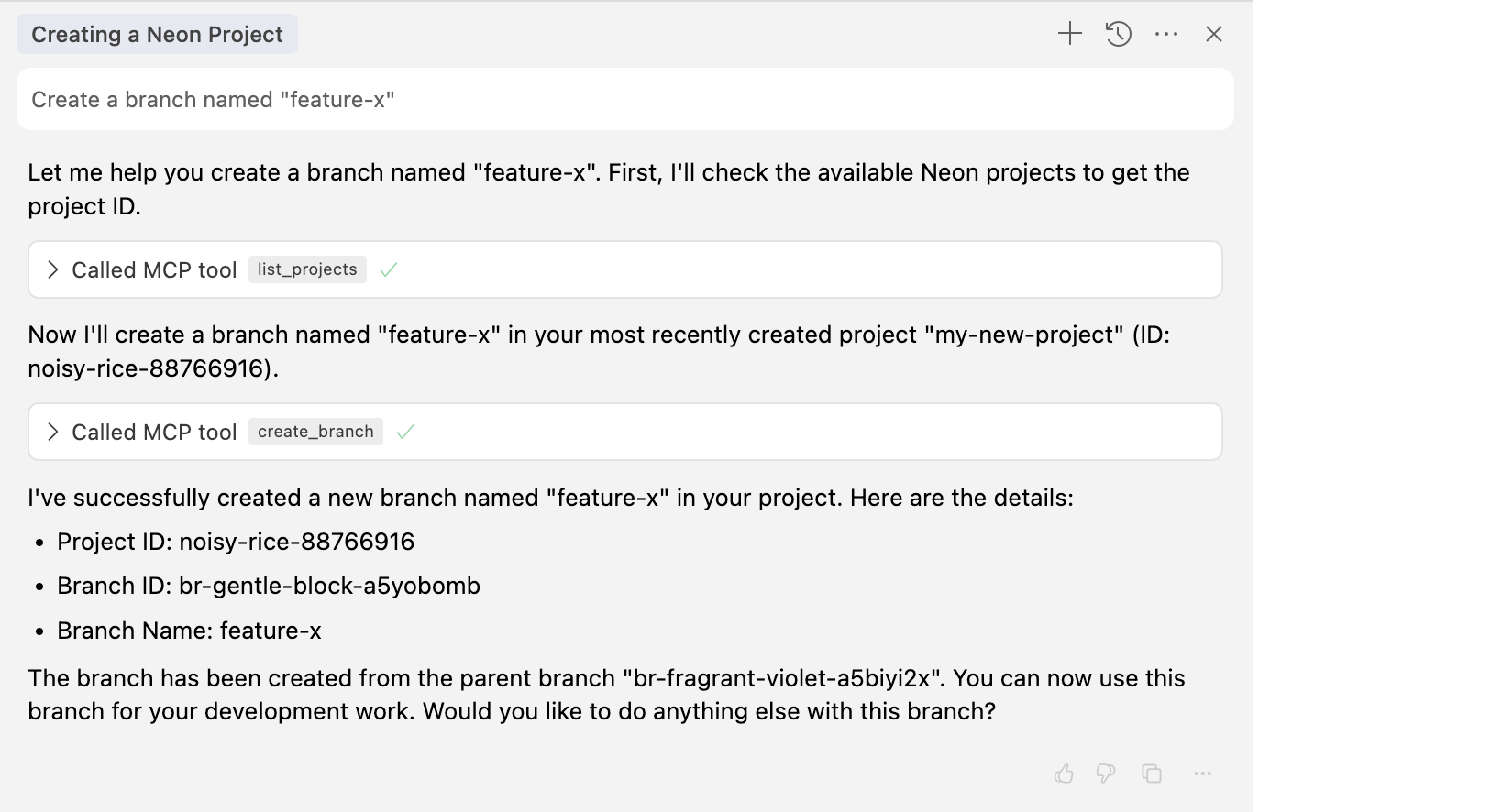
Cursor will use the `create_branch` MCP tool to create the branch and provide you with the branch name and ID. Notice how we don't need to specify the project ID, as Cursor remembers the active project context.
## Conclusion
Cursor combined with the Neon MCP Server, whether using the **Remote Hosted** option or the **Local Server** setup, lets you use natural language to interact with your database and take advantage of Neon's branching capabilities for fast iteration. This approach is ideal for quickly testing
database ideas and making schema changes during development.
## Resources
- [MCP Protocol](https://modelcontextprotocol.org)
- [Adding an MCP Server to Cursor](https://docs.cursor.com/context/model-context-protocol)
- [Neon Docs](/docs)
- [Neon API Keys](/docs/manage/api-keys#creating-api-keys)
- [Neon MCP server GitHub](https://github.com/neondatabase/mcp-server-neon)
Note: This uses OAuth (not API key), so you'll need to approve each MCP action. For fewer prompts, use Quick Setup above.
### Option 1: Setting up the Remote Hosted Neon MCP Server (OAuth)
By default, the Remote MCP Server connects to your personal Neon account. To connect to an organization's account, you must authenticate with an API key. For more information, see [API key-based authentication](/docs/ai/neon-mcp-server#api-key-based-authentication).
This method uses Neon's managed server and OAuth authentication.
1. Open Cursor.
2. Create a `.cursor` directory in your project's root directory. This is where Cursor will look for the MCP server configuration.
3. Paste the following JSON configuration into a file named `mcp.json` in the
`.cursor` directory:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"url": "https://mcp.neon.tech/mcp",
"headers": {}
}
}
}
```
If you have other MCP servers configured, you can copy just the `Neon` part.
Save the `mcp.json` file after pasting the configuration.
4. **Restart Cursor** or reload the window (`Developer: Reload Window` from the Command Palette). If Cursor prompts you to Enable the MCP server, click **Enable**.
5. An OAuth window will open in your browser. Follow the prompts to authorize Cursor to access your Neon account.

6. You can verify that the connection is successful by checking the **Tools & MCP** section in Cursor settings.

7. Cursor is now connected to Neon's remote MCP server.
### Option 2: Setting up the Local Neon MCP Server
This method runs the Neon MCP server locally on your machine, using a Neon API key for authentication.
1. Open Cursor.
2. Create a `.cursor` directory in your project's root directory. This is where Cursor will look for the MCP server configuration.
3. Paste the following JSON configuration into a file named `mcp.json` in the `.cursor` directory. Replace `` with your actual Neon API key which you obtained from the [prerequisites](#prerequisites) section:
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@neondatabase/mcp-server-neon", "start", ""]
}
}
}
```
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"command": "cmd",
"args": [
"/c",
"npx",
"-y",
"@neondatabase/mcp-server-neon",
"start",
""
]
}
}
}
```
```json
{
"mcpServers": {
"Neon": {
"command": "wsl",
"args": ["npx", "-y", "@neondatabase/mcp-server-neon", "start", ""]
}
}
}
```
If you have other MCP servers configured, you can copy just the `Neon` part.

4. Save the `mcp.json` file after pasting the configuration.
5. **Restart Cursor** or reload the window (`Developer: Reload Window` from the Command Palette).
6. Cursor is now connected to Neon's MCP server. You can verify that the connection is successful by checking the **MCP Servers** section in Cursor settings.

You've now configured Neon MCP Server in Cursor and can manage your Neon Postgres databases using AI.
### Verification
Now that you have the Neon MCP server set up either remotely or locally, you can verify the connection and test the available tools.
1. Open a Cursor **Chat** using the keyboard shortcut **Command + I** (on Mac) or **Control + I** (on Windows) and select the **Agent** option from the drop-down menu.

2. Type `List your available MCP tools` in the Composer text field, select the **agent** option in the corner of the field, and click **Submit**.
**_Note: The agent option here is tiny and easy to miss!_**

3. Try out an Neon MCP Server tool by typing `Tell me about my Neon project `. **You'll need to provide your Neon project ID.**

Cursor uses the Neon MCP Server `describe_project` tool to retrieve your project's details.
### Global MCP Server in Cursor
You can also set up a global MCP server in Cursor. This allows you to use the same MCP server configuration across all your projects. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Open Cursor.
2. Go to the **Settings**.
3. In the **Tools & MCP** section, click on **+ Add Custom MCP**.
4. Paste the same JSON configuration either for the **Remote Hosted** or **Local MCP Server** (as shown in the previous sections) into the configuration field.
5. Save the configuration.
6. Restart Cursor or reload the window (`Developer: Reload Window` from the Command Palette).
7. You now have Neon MCP Server set up globally in Cursor. You can use it in any project without needing to configure it again for each project.
### Troubleshooting
If you are on a version of Cursor that does not support JSON configuration for MCP servers, you can use the following command when prompted:
```bash
npx -y @neondatabase/mcp-server-neon start
```
These actions enable any MCP client like Cursor to interact with various functionalities of the **Neon platform via the Neon API.** Certain tools, especially database migration ones, are tailored for AI agent and LLM usage, leveraging Neon’s branching for safe preview and commit.
## Development Workflow: Adding a Column with Cursor and Neon MCP
Let's walk through a typical development scenario: Quickly adding a column for prototyping using natural language within Cursor. The following chat log demonstrates a real interaction with Cursor and the Neon MCP server.
**Scenario:** During development, you decide to track timestamps for entries in your `playing_with_neon` table. You want to quickly add a `created_at` column.
Use `⌘I` to open Cursor's Composer and `⌘N` to create a new Composer.
For your security, review the tool's purpose before permitting the operation to proceed. Remember that LLMs can sometimes produce unexpected results, so careful monitoring is always recommended.
Here's the conversation log between the user and Cursor:
```text shouldWrap
User: In my neon project id: round-salad-44063611 list all the tables
Cursor: I'll help you list all the tables in your Neon project. I'll use the default database name 'neondb' since none was specified.
> Called MCP Tool (get_database_tables)
> I found one table in your database:
> playing_with_neon (in the public schema)
> Would you like to see more details about this table's structure or perform any other operations with it?
User: Can you show me first 5 rows?
Cursor: I'll query the first 5 rows from the playing_with_neon table.
> Called MCP Tool (run_sql)
> Here are the first 5 rows from the table. The table has three columns:
> id (sequential numbers)
> name (string values)
> value (decimal numbers)
> Would you like to perform any other operations with this data?
User: can you add a created_at column?
Cursor: I'll help you add a created_at column to the playing_with_neon table. I'll set it up with a timestamp data type and set it to automatically record the creation time of new rows.
> Called MCP Tool (prepare_database_migration)
> Let me verify the change in the temporary branch to make sure it was applied correctly.
> Called MCP Tool (run_sql)
> I've added the created_at column to the playing_with_neon table in a temporary branch. Would you like to commit this migration to the production branch?
> Migration Details:
> Migration ID: a65babcd-d1cc-401f-89b5-762570570102
> Temporary Branch Name: br-silent-cherry-a1eqrl6i
> Temporary Branch ID: br-silent-cherry-a1eqrl6i
> Migration Result: Success
> Please let me know if you'd like to proceed with applying this change to the production branch.
User: yeah do it
Cursor: I'll complete the migration and apply the changes to the production branch.
> Called MCP Tool (complete_database_migration)
> The migration has been successfully completed! The created_at column has been added to your table in the production branch, and the temporary branch has been cleaned up.
```
**Key takeaways:**
- **Natural language interaction:** You can use simple, conversational English to interact with your database.
- **Step-by-step guidance:** Cursor (Claude) confirms each step and provides details like branch names and migration IDs.
- **MCP Tools in Action:** The underlying MCP tools (`get_database_tables`, `run_sql`, `prepare_database_migration`, `complete_database_migration`) illustrate the automated process.
- **Branching for safety:** The agent automatically creates a temporary branch for schema changes. The user will be prompted to confirm the migration before applying it to the production branch.
You can verify the changes in your Neon Console or by querying the database directly.

While the Neon MCP server allows you to utilize all of Neon's functionalities, you can also use a [generic Postgres MCP server](https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/servers/tree/main/src/postgres) to connect to Neon.
## Bonus: Creating a project and branch
Beyond schema changes, you can also manage your Neon projects and branches directly within Cursor using natural language commands. This can be useful for quickly setting up a new development or test environment.
### Creating a new project
Let's say you want to create a new Neon project named "my-new-project". You can simply tell Cursor:
```text shouldWrap
User: Create a Neon project named "my-new-project"
Cursor: I'll help you create a new Neon project with the specified name.
> Called MCP Tool (create_project)
> Great! I've created a new Neon project for you with the name "my-new-project". Here are the important details:
> Project ID: orange-dawn-33739962
> Default branch: main
> Default database: neondb
> The project is ready to use. You can start creating tables and working with your database right away.
```

Cursor will then use the `create_project` MCP tool to initiate the project creation. It will provide you with a project ID and name.
### Creating a New Branch
Once you have a project, you can easily create new branches for development or experimentation. For example, to create a branch named "feature-x" in your "my-new-project" project:
```text shouldWrap
User: Create a branch named "feature-x"
Cursor: Perfect! I've created a new branch named "feature-x". Here are the details:
> Branch ID: br-cold-mountain-a523ka2w
> Branch name: feature-x
> Parent branch ID: br-odd-pine-a5y53krm
> The branch has been created successfully and is ready for use.
```

Cursor will use the `create_branch` MCP tool to create the branch and provide you with the branch name and ID. Notice how we don't need to specify the project ID, as Cursor remembers the active project context.
## Conclusion
Cursor combined with the Neon MCP Server, whether using the **Remote Hosted** option or the **Local Server** setup, lets you use natural language to interact with your database and take advantage of Neon's branching capabilities for fast iteration. This approach is ideal for quickly testing
database ideas and making schema changes during development.
## Resources
- [MCP Protocol](https://modelcontextprotocol.org)
- [Adding an MCP Server to Cursor](https://docs.cursor.com/context/model-context-protocol)
- [Neon Docs](/docs)
- [Neon API Keys](/docs/manage/api-keys#creating-api-keys)
- [Neon MCP server GitHub](https://github.com/neondatabase/mcp-server-neon)